Resources from the Movie:
Our Brains Are No Match for Our Technology by Tristan Harris, New York Times
The Dark Psychology of Social Networks by Jonathan Haidt, The Atlantic
Surveillance Capitalism by Shoshana Zuboff, Harvard Business Review
The Truth About Algorithms by Cathy O’Neill, RSA
Want to Work for Google? You Already Do. by Joe Toscano, TEDx Talks
Free Speech Is Not The Same As Free Reach by Renée DiResta, Wired
Ten Arguments for Deleting Your Social Media Accounts Right Now by Jaron Lanier
Weapons of Math Destruction by Cathy O'Neil
Here is the Stanford University Behavior Design Lab featured in the movie.
Stanford U. Persuasion Through Mobile Design Lab is run by BJ Fogg, behavior scientist at Stanford, https://www.bjfogg.com/
In 2006 we created a video to warn the FTC (and others) about problematic areas related to persuasive technology. See the video here: https://vimeo.com/117427520
(BJ’s quick note: This video above has a slow pace, and it’s not my best look, with the shaved head and all. However, do listen to what I was predicting and warning people about. At least go to minute 10 and see what I say about the political use of persuasion profiles. We recorded this video in 2006 to warn policymakers of the impacts persuasive technology could have. Remember, this message was recorded in 2006 not 2016 and the message rings true more and more every day.)
Simone Stolzoff from Wired (2018) explains in The Formula for Phone Addiction Might Double As a Cure,
Ten years ago, a Stanford lab created the formula to make technology addictive. Now, Silicon Valley is dealing with the consequences.
"IN SEPTEMBER 2007, 75 students walked into a classroom at Stanford. Ten weeks later, they had collectively amassed 16 million users, $1 million dollars in advertising revenue, and a formula that would captivate a generation. The class—colloquially known as "The Facebook Class"—and its instructor, BJ Fogg, became Silicon Valley legends."
False News Travels Faster Than True Stories On Twitter
Research project finds humans, not bots, are primarily responsible for spread of misleading information.
“We found that falsehood diffuses significantly farther, faster, deeper, and more broadly than the truth, in all categories of information, and in many cases by an order of magnitude,” says Sinan Aral, a professor at the MIT Sloan School of Management and co-author of a new paper detailing the findings."
- Uninstall apps from my phone that are wasting your time such as social media apps and news apps.
- Turn off notifications. Turning off all notifications. I’m not using Google anymore, I’m using Qwant, which doesn’t store your search history.
- Never accept a video recommended to you on YouTube. Always choose. There are tons of Chrome extensions that remove recommendations.
- Before you share, fact-check, consider the source, do that extra Google. If it seems like it’s something designed to really push your emotional buttons, like, it probably is. Essentially, you vote with your clicks. If you click on clickbait, you’re creating a financial incentive that perpetuates this existing system.
- Make sure that you get lots of different kinds of information in your own life. I follow people on Twitter that I disagree with because I want to be exposed to different points of view.
- From Spike Blog, Take a Break From Tech, the Benefits of a Digital Detox (2021), "the average user touches his phone no less than 2,617 times per day"
- From Lifehacker, How to Take A Digital Break (2021)
- From Berkley's Greater Good Magazine, Five Reasons to Take a Break From Screens (2018),
- From CNN, Treat Your Phone Like a Bad Relationship and Breakup (2023)
Try to take a digital break and take note of how you are affected. What do you experience while on the break?
Open this link and think about what is true for you. Below are some charts from the findings, some things to write about include your thoughts about the findings and in what ways these are either true or different for you:
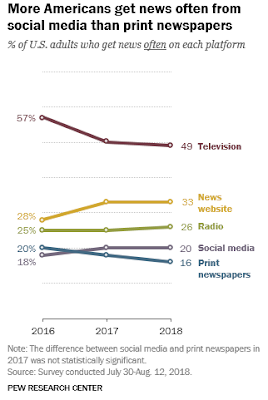
A 2021 PEW study showing social media use and news.
More Americans get news on social media than from print newspapers. In 2018, one-in-five adults said they often get news on social media. And Facebook continues to dominate as the most common social media site used for news by Americans: About four-in-ten Americans (43%) get news on this site.Which of the platforms in the graph above do you often get your news from?
The growing trend of getting news online is particularly concerning because a 2020 study found that:
Americans Who Mainly Get Their News on Social Media Are Less Engaged, Less Knowledgeable
Those who rely on social media for news are less likely to get the facts right about the coronavirus and politics and more likely to hear some unproven claims.
See this post for a list of research-based conclusions why digital media is bad for your learning and your grades












No comments:
Post a Comment